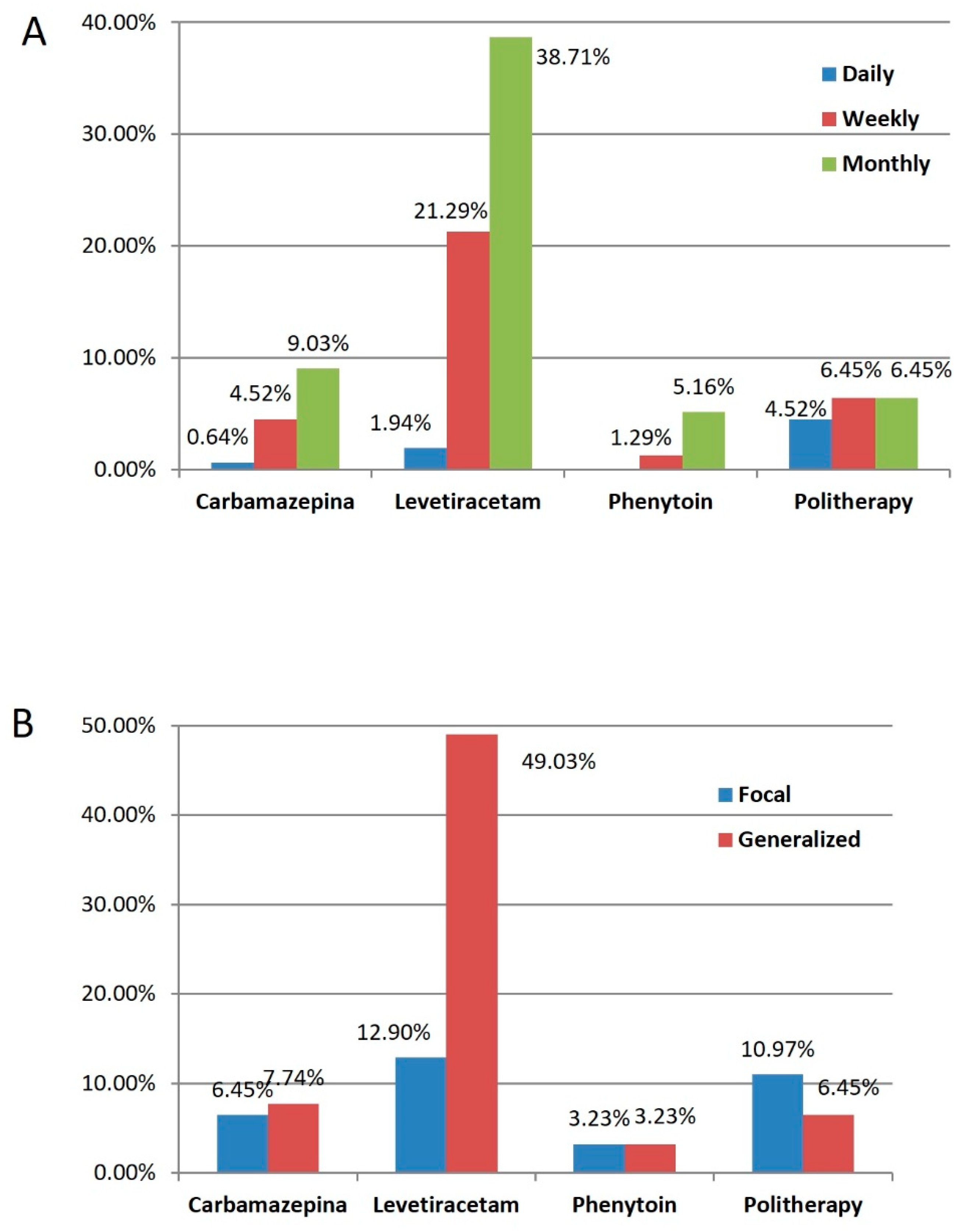
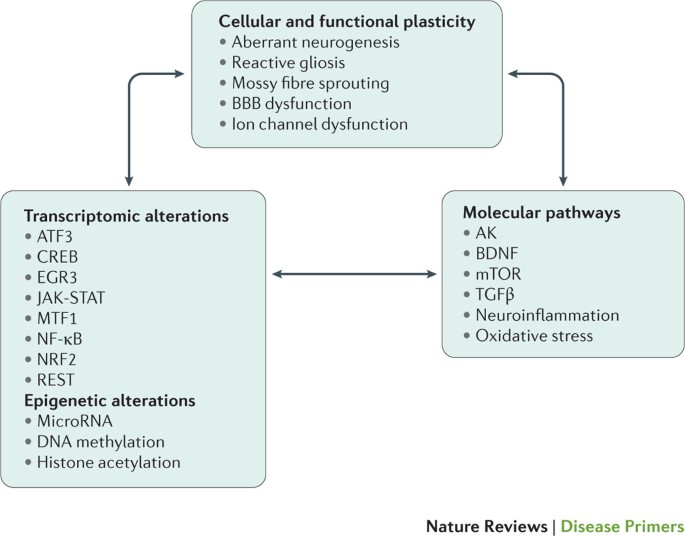
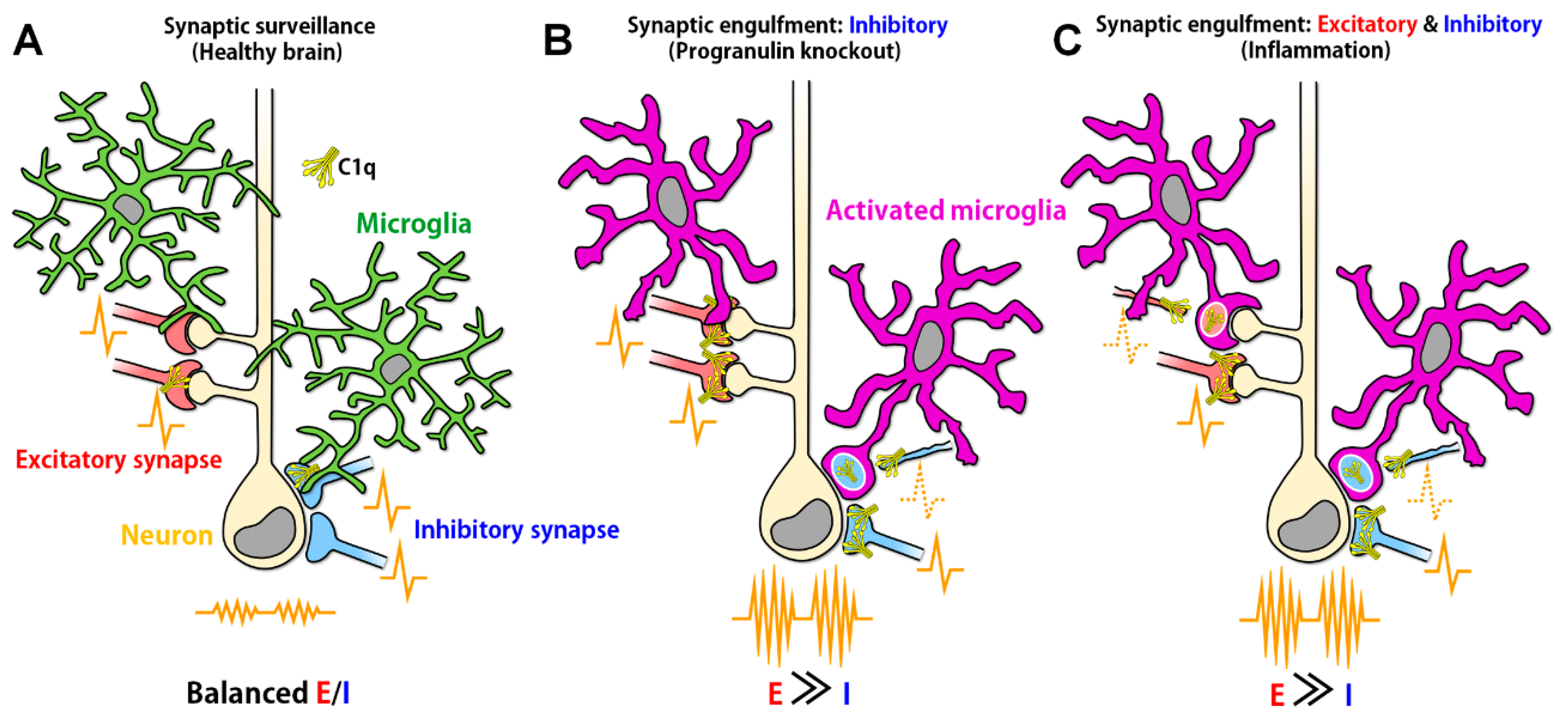
Abstract For Epilepsy And Anesthesia Developmental Psychology
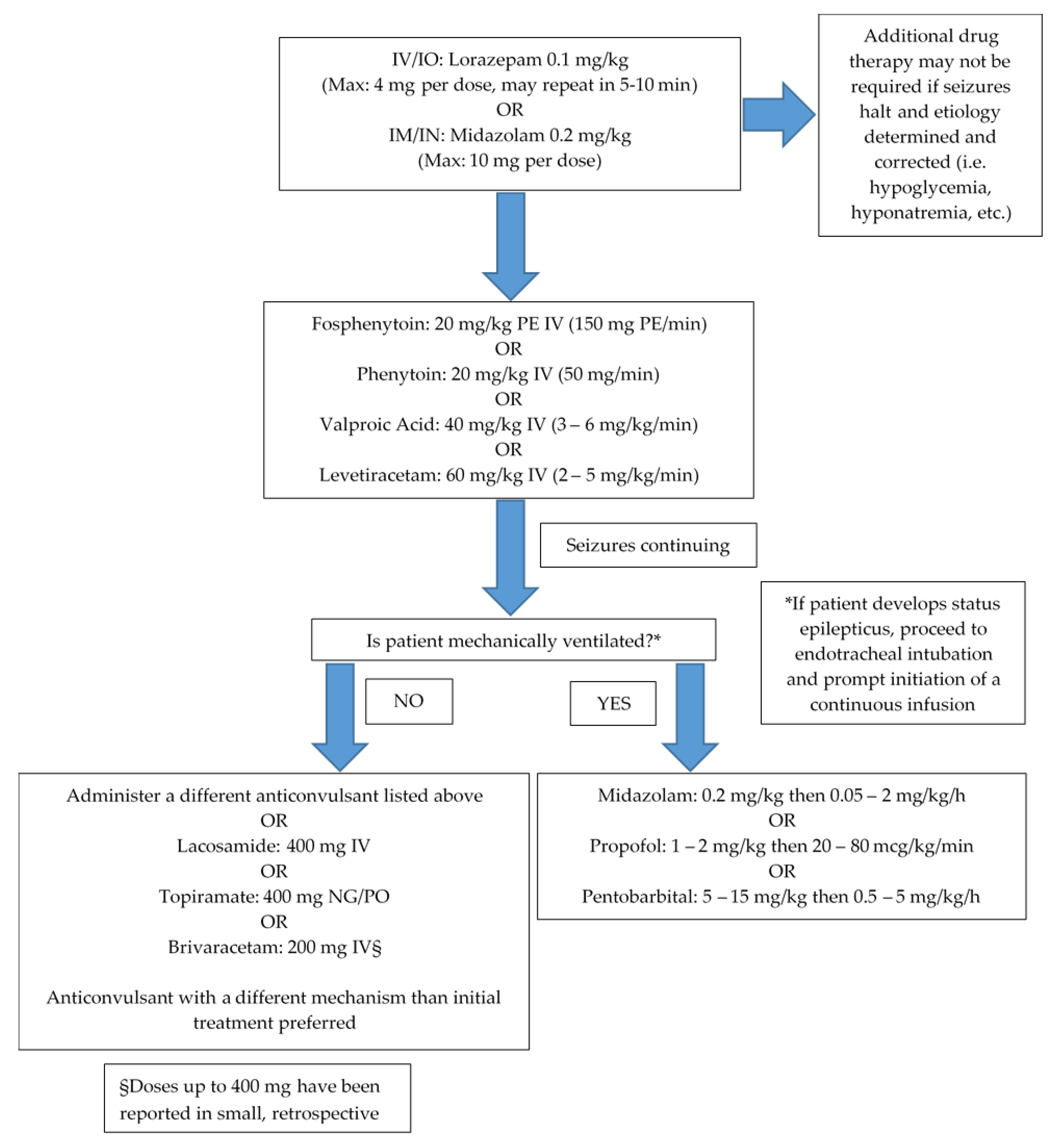
However there have been reports of postoperative convulsions that appeared to be caused by anesthetic or analgesic drugs administered intraoperatively via injection or inhalation.

Abstract for epilepsy and anesthesia developmental psychology. In general when seizures occur during surgery their onset often coincides with the introduction of a specific anesthetic or analgesic drug. Epilepsy is a common neurological condition that anaesthetists will frequently encounter in both the elective and emergency setting. Epilepsy is the most common serious neurological disorder with a prevalence of 05 1 of the population. While the traditional antiepileptic drugs aeds still play a significant role in.
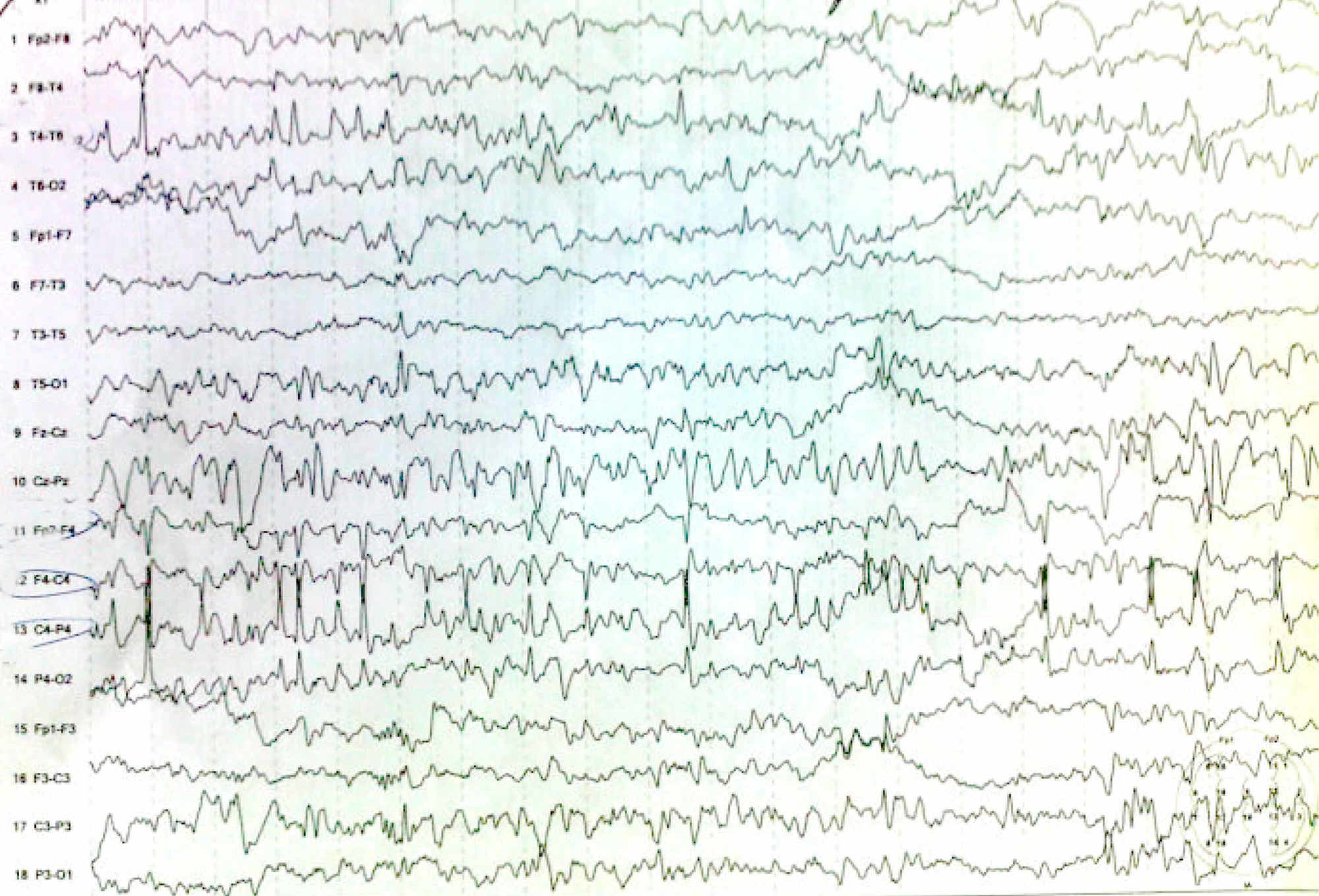
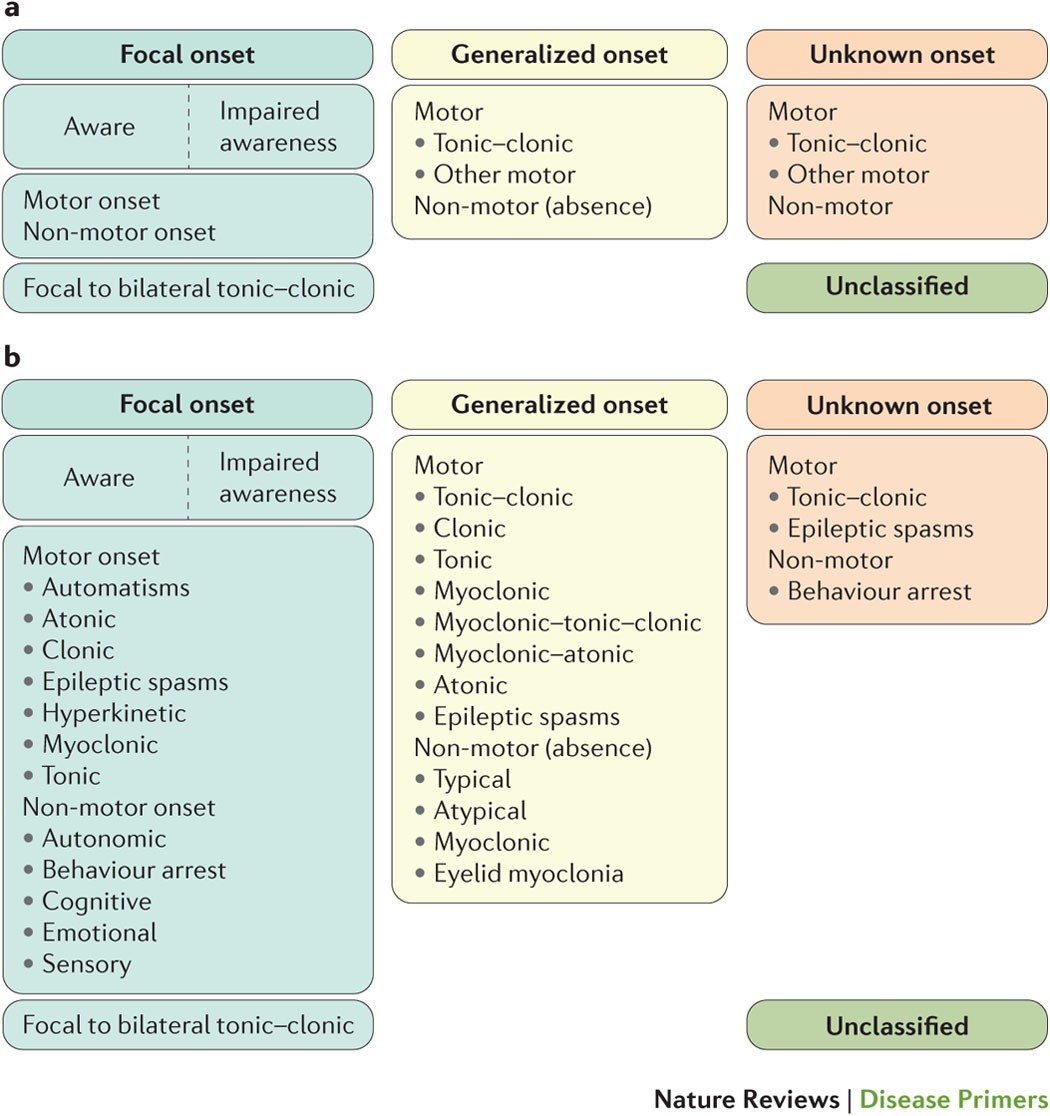
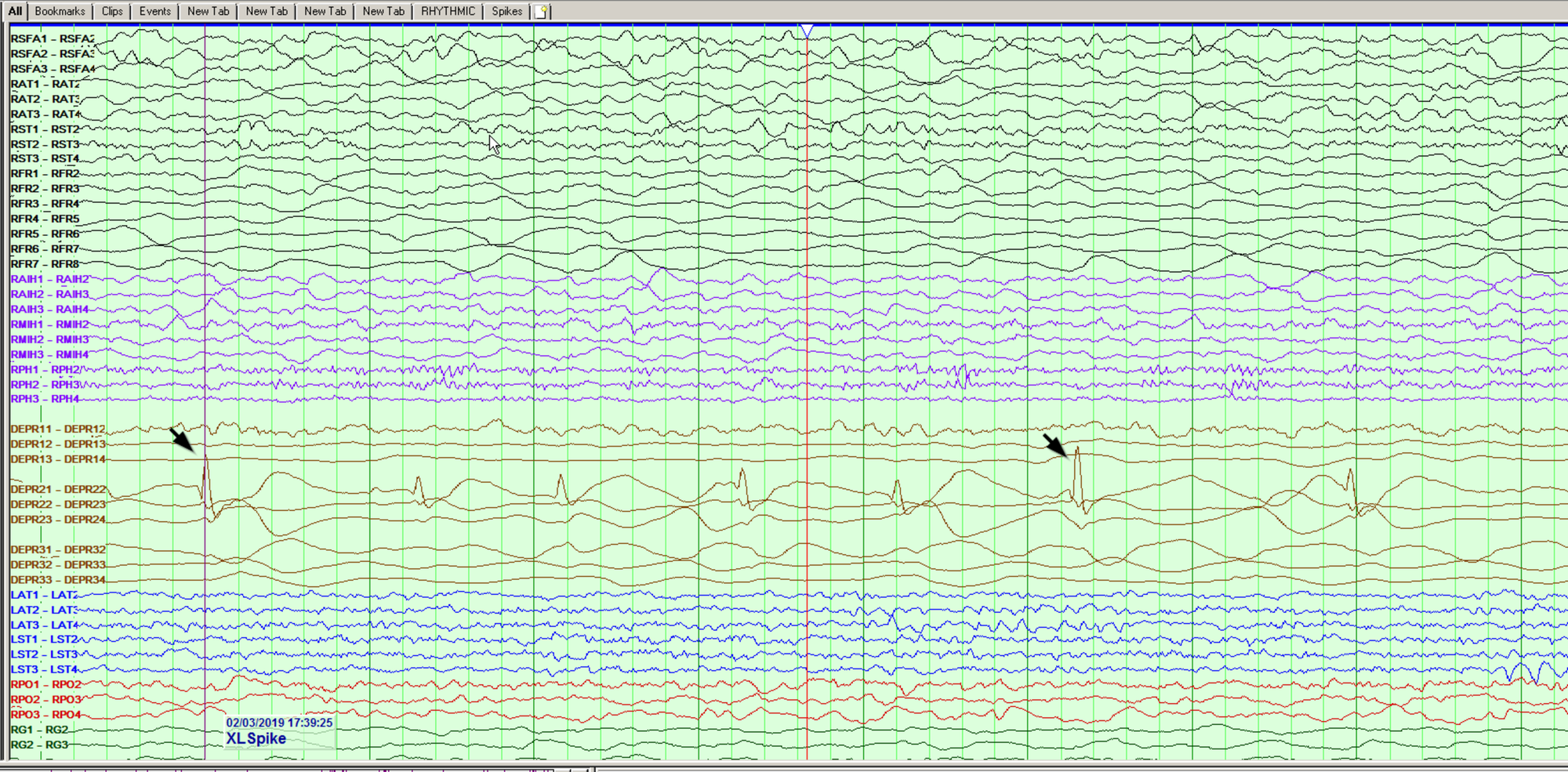
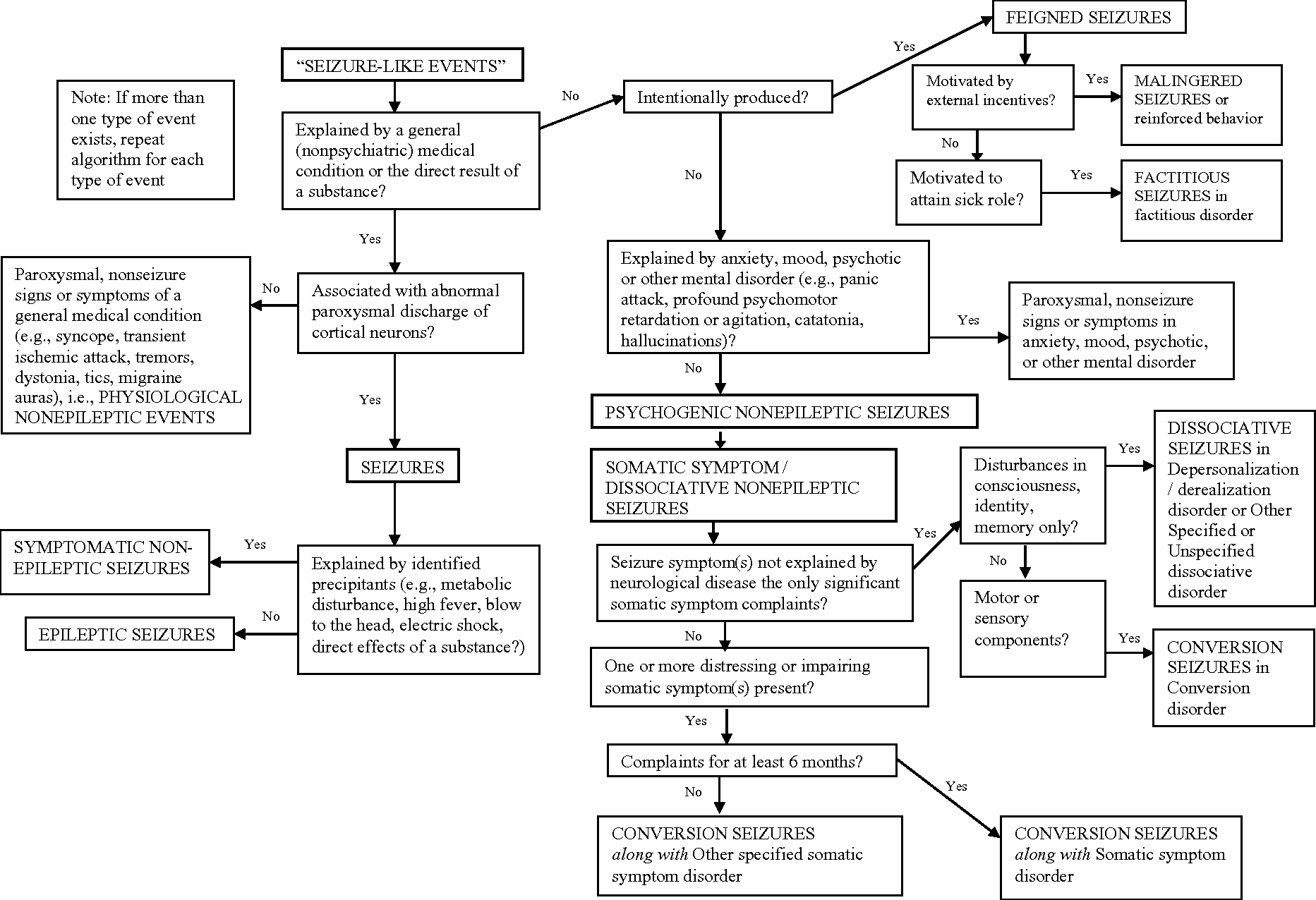
Epilepsy is a clinical disorder of paroxysmal recurring seizures the diagnosis excluding alcohol or drug withdrawal seizures or such recurring exogenous events as repeated insulin induced hypoglycemia. Anesthesia for epilepsy surgery may be required either in the form of general anesthesia or local. Some anesthetics may possess proconvulsant properties anticonvulsant. Patients with epilepsy may experience breakthrough seizures in the perioperative period but psychogenic non epileptic attacks can also occur in this setting.
Epilepsy has a profound impact on each individual diagnosed with this disease. New antiepileptic drugs aeds have been a major change in the approach to. Patients with epilepsy may experience breakthrough seizures in the perioperative period but psychogenic non epileptic attacks can also occur in this setting. Proconvulsant and anticonvulsant properties have been reported for virtually every anesthetic such that these properties become elements.
Understanding the pathophysiology of epilepsy and its pharmacological therapies enables safe planning and delivery of care. While certain anaesthetic agents can provoke seizures recovery from anaesthesia can be associated with shivering and myoclonus which does not indicate epilepsy. The primary concerns for providing anesthesia to the patient with epilepsy are the capacity of anesthetics to modulate or potentiate seizure activity and the interaction of anesthetic drugs with aeds. Children with frontal lobe epilepsy adnfle caused by kcnt1 have onset of seizures before adolescence but later than children with kcnt1 related developmental and epileptic encephalopathyin these children delays in achieving developmental milestones during infancy or early childhood may be the first sign of a kcnt1 related epilepsyseizures typically arise out of sleep and occur in clusters.
While certain anaesthetic agents can provoke seizures recovery from anaesthesia can be associated with shivering and myoclonus which does not indicate epilepsy. In the developed countries predominant causes include developmental disorders and idiopathic causes in children and vascular and degenerative causes in adults.