Abstract Electric Potential Lab
V frac14pivarepsilon0 fracqr tag3 the electric potential has magnitude but no direction.
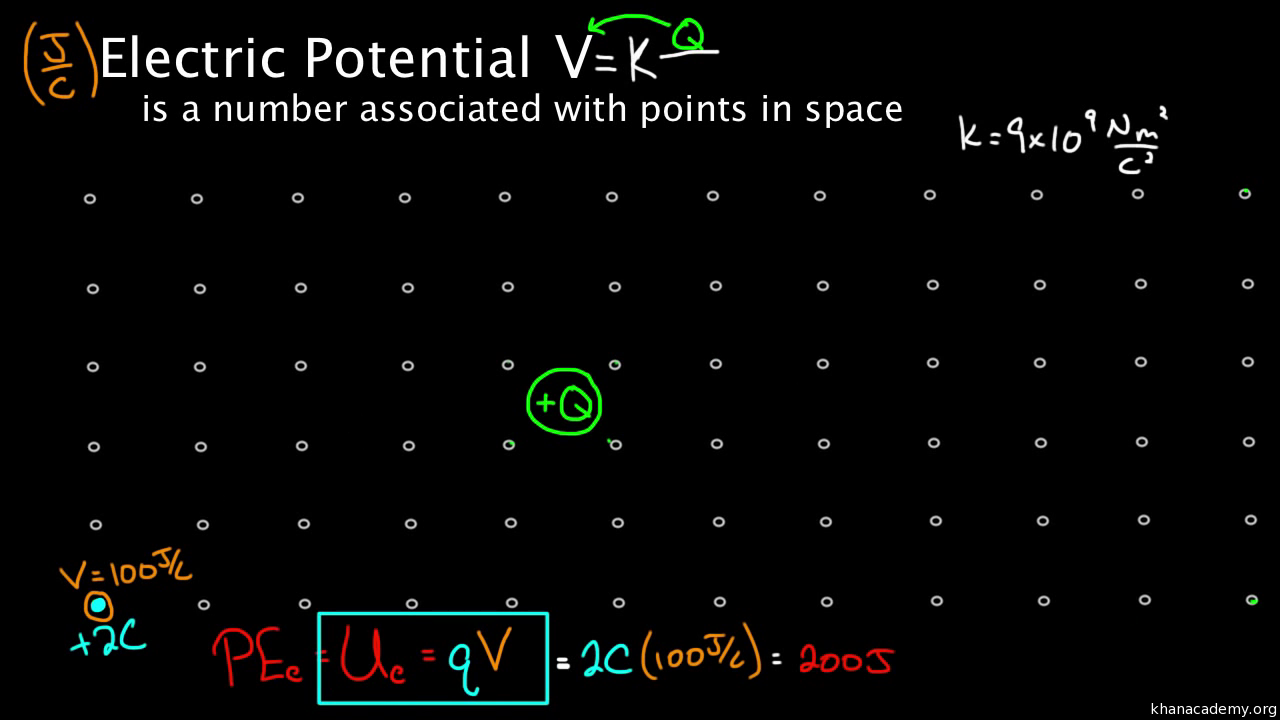
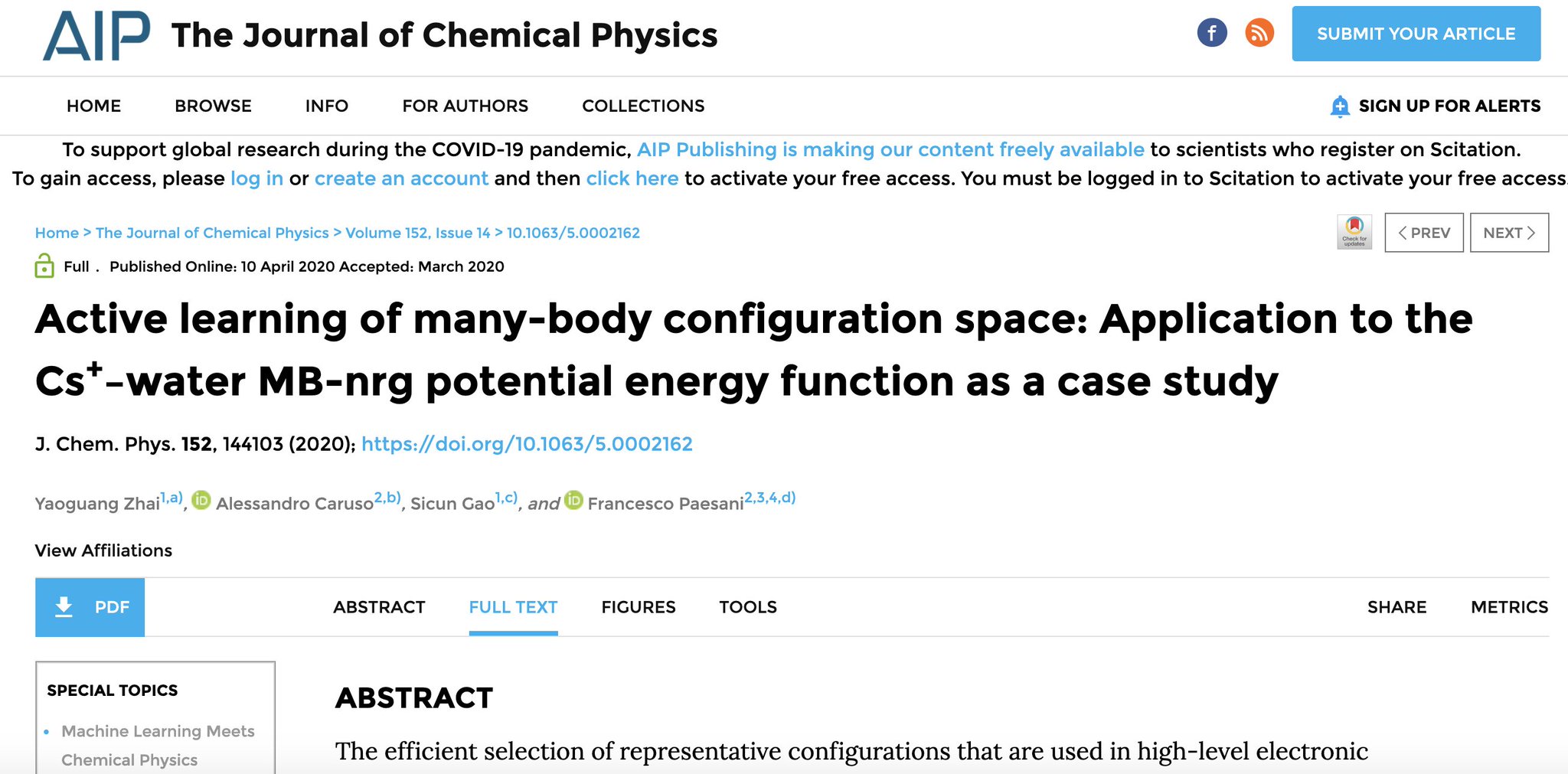
Abstract electric potential lab. The electric potential or simply potential is dened as the electric potential energy u divided by the charge q. This equation also shows that electric field is equal to change in potential divided by change in distance. The unit of the electric potential is the joulescoulomb volt v. For a point source the electric potential is given by.
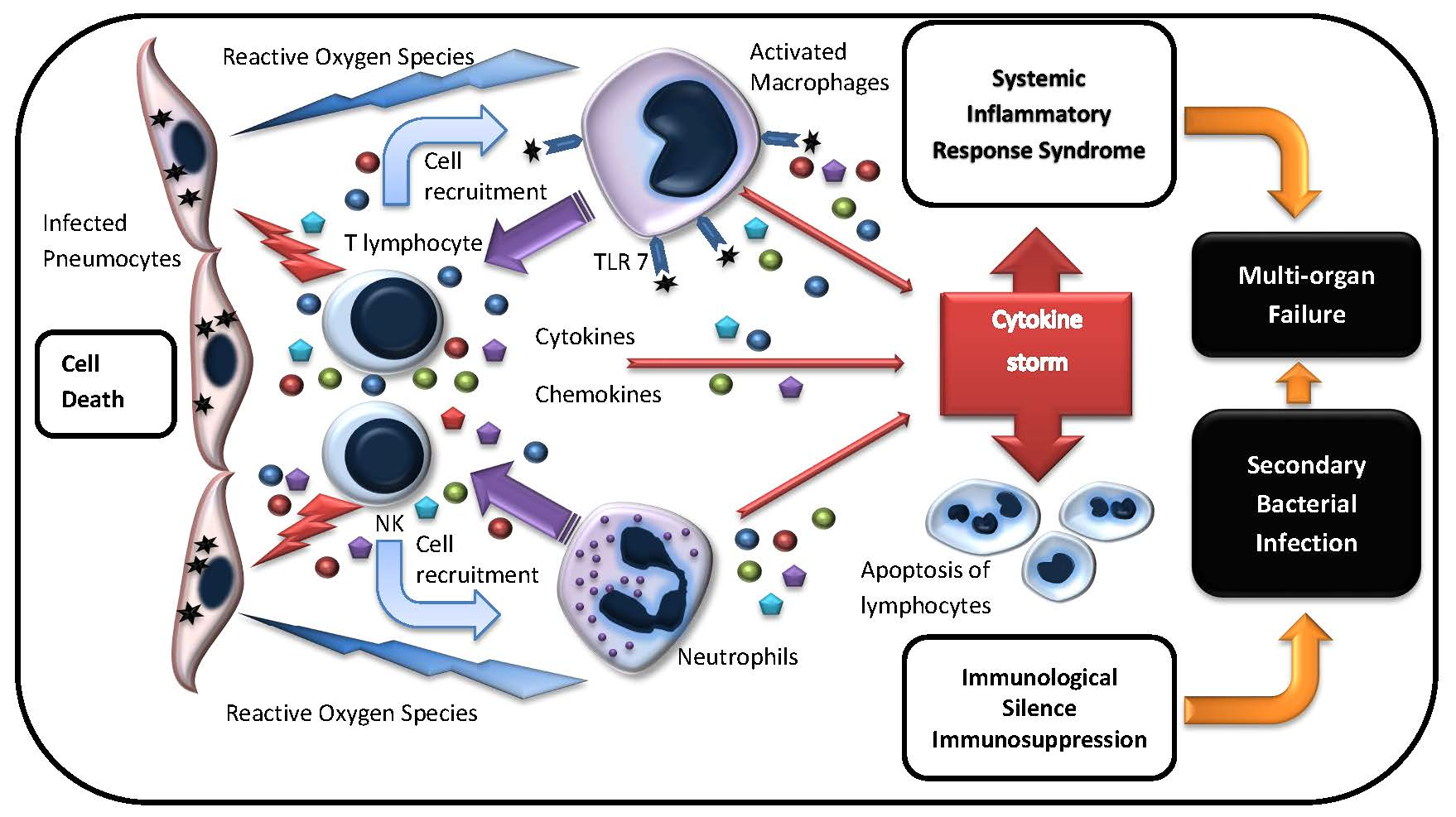
In a sense positive charges are sources of positive electric potential while negative charges are sources of negative electric potential. Any charge placed in an electric field will experience a force as will any mass placed in a gravitational field. Electric and potential fields objective. Exerted on other charged particles.
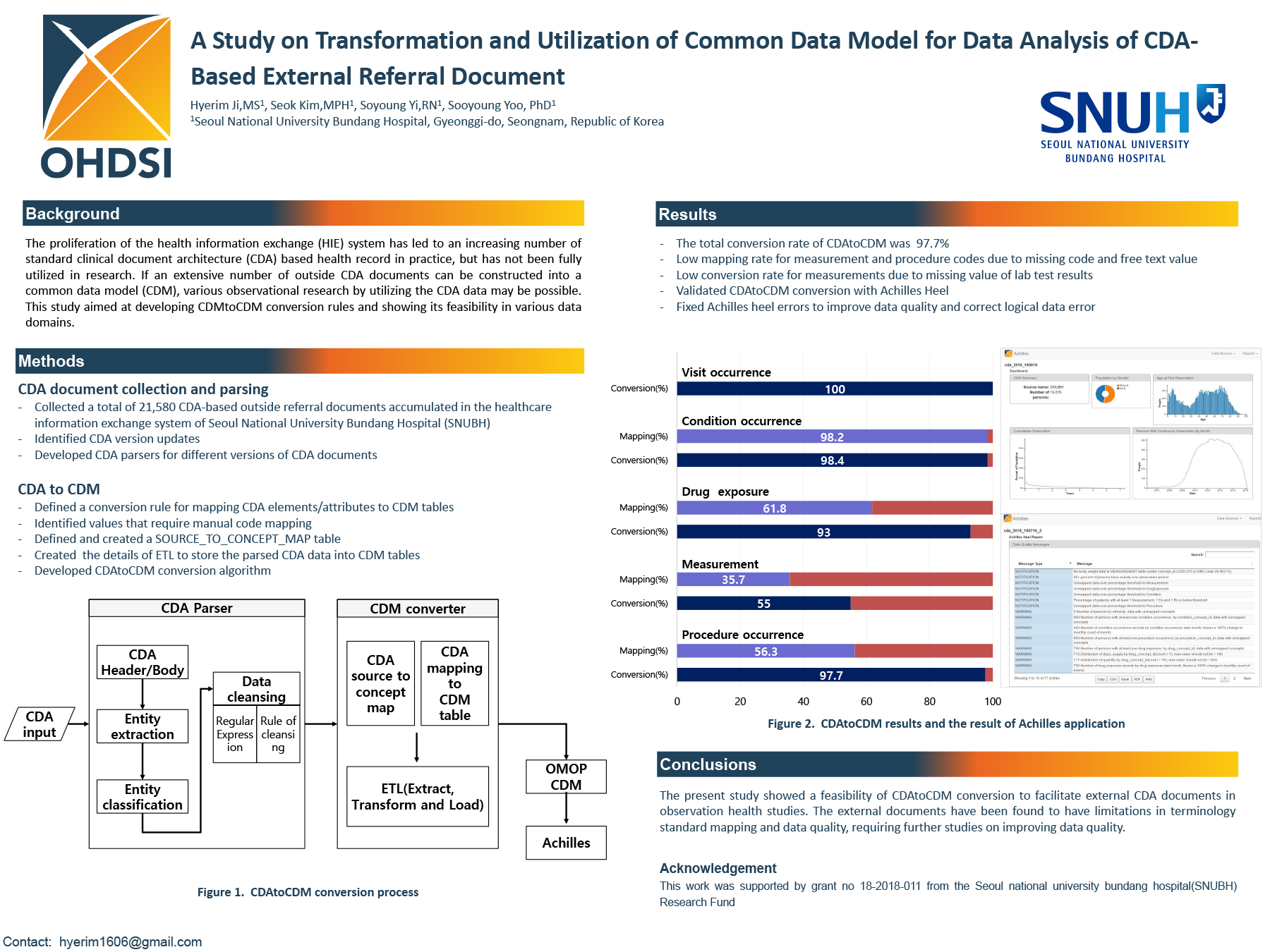
This visualization shows how different arrangements of charges can lead to very different looking contour maps of potential and electric fields. According to the data analysis the electric field was approximately 1317 vcm and a theoretical value of 1343 vcm which provided a 194 difference. Electric potential of a point at a distance r from charge q is given by. The probe that you will use in this lab called a digital multimeter directly measures the electric potential differencebetween two points near a charge distribution.
V kq r 2 where k is a constant. Electric potential voltage before discussing electric potential it is useful to recall the more intuitive concept of potential energy in particular gravitationalpotential energy. A surface over which the electric potential is constant is called an equipotential surface. Every charged particle has a region surrounding it known as the electric field where forces are.
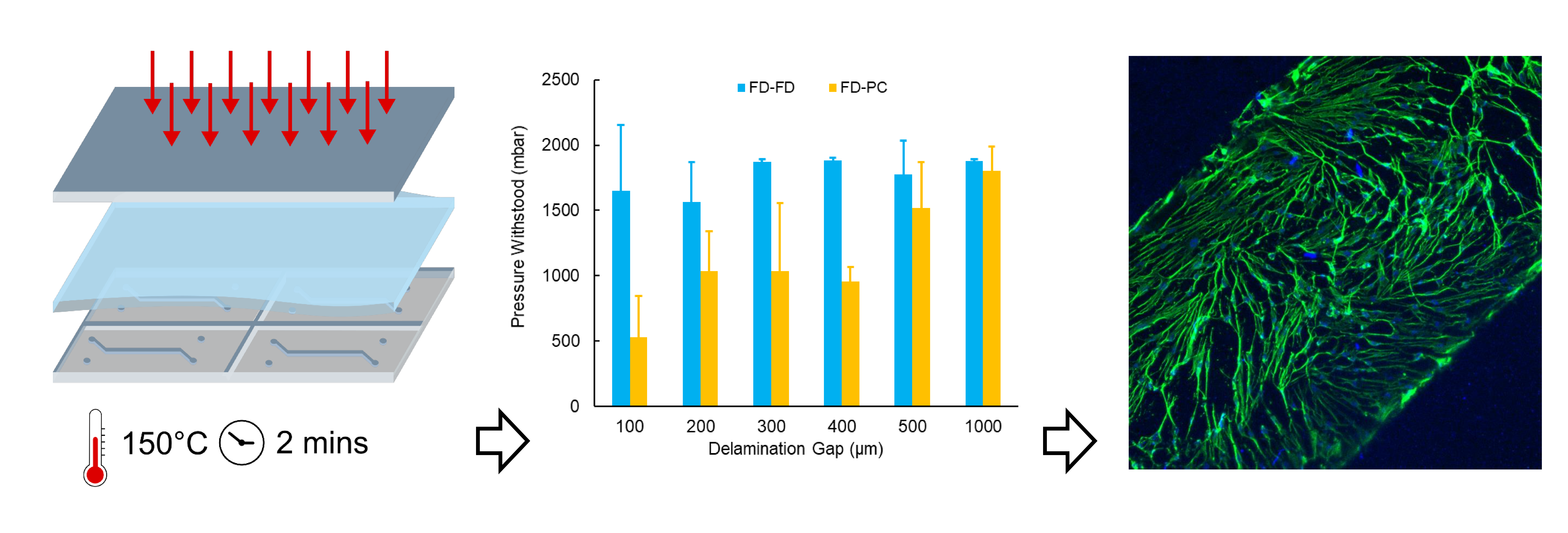
In this experiment we confined these measurements to a plane which we will form equipotential lines. Just as mass in a gravitational field has some potential energy so does a charge in an electric field. In this lab this was accomplished for an. In this lab we will examine some aspects of electric field and electric potential.
In this lab we will study another way of thinking about this interaction through electric potentials. As in the image below the. Abstract in this lab we studied how electric potential can be mapped out as lines of points with equal potential differences and electric fields. Electric field maps can be produced by mapping an electric fields equipotential lines and then connecting them with electric field lines.
To represent this field graphically lines of equal electric potential called equipotential lines are drawn around the source charge.